New Map Details Extreme Rainfall and Risk of Flooding on Thousands of North Carolina’s Hog and Poultry Facilities
By: Waterkeeper Alliance
Analysis of Operations in and nearby Floodplains Reveals the Potential Inundations of Thousands of Waste Cesspools Holding Hundreds of Millions of Gallons of Manure and Urine
Hurricane Florence’s torrential rains pelted parts of North Carolina that are home to more than 1,500 industrial animal operations with over 1,000 nearby waste storage cesspools. These operations have the potential to annually produce as much as 4 billion gallons of wet swine waste and 400 thousand tons of dry poultry litter, an exclusive analysis by EWG and Waterkeeper Alliance reveals.
The organizations overlaid locations of concentrated animal feeding operations with government rainfall estimates to produce an interactive map that details Florence’s potential impact on vulnerable operations in the state. Clicking and zooming in on a location shows the estimated amount of rain each operation received from Sept. 14, when Florence made landfall, through Sept. 16, and the potential amount of waste produced or stored at each site.
The groups calculated the potential waste stored at each site by using North Carolina permit data, the USDA Agricultural Census, and manure production rate data from the North Carolina Agricultural Chemicals Manual. A link to the methodology is here.
Among our findings:
- There are 926 concentrated hog feeding operations housing over 3.8 million pigs and 578 industrial poultry operations holding an estimated 35 million poultry in areas where the National Weather Service said flooding was “occurring or imminent” after Florence. Livestock at those 1,504 concentrated animal feeding operations are capable of producing 4 billion of gallons of wet waste and over 400,000 tons of dry litter each year. More than a third of those sites received an estimated 15 to 19 inches of rain, and more than one-fourth saw more than 20 inches.
- There are 123 hog industrial hog operations and 40 industrial poultry operations in or within 500 feet of the 100-year floodplain that received at least 15 inches of rain. Livestock at those 163 sites are capable of producing more than 395 million gallons of liquid waste and more than 27,000 tons of dry waste a year.
- Federal standards require waste pits in North Carolina to be designed to withstand a so-called 24-hour/25-year rain event without releasing manure. In areas where the National Weather Service said flooding was occurring or imminent, more than 1,000 waste pits received more rain than the 24-hour/25-year rain event defined for that location. Of those, an estimated 35 pits are in the 100-year floodplain and received over 15 inches of rain. Those pits alone are capable of holding more than 129 million gallons of animal waste.
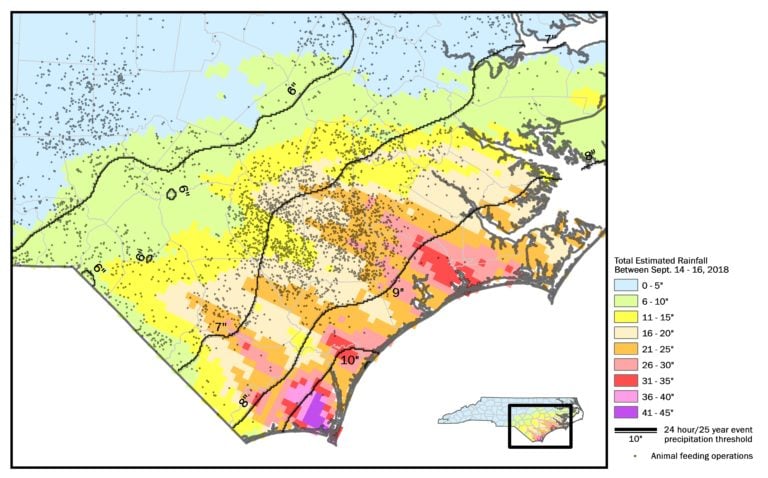
- The map below shows colored bands of estimated rainfall amounts in North Carolina’s coastal plain from Sept. 14-16. The dark diagonal lines show the zones of rainfall expected during a 24-hour/25-year rain event. In all of the zones except for the one with the lowest expected rainfall (in blue), the total estimated rainfall was well in excess of what the waste pits were designed to withstand.
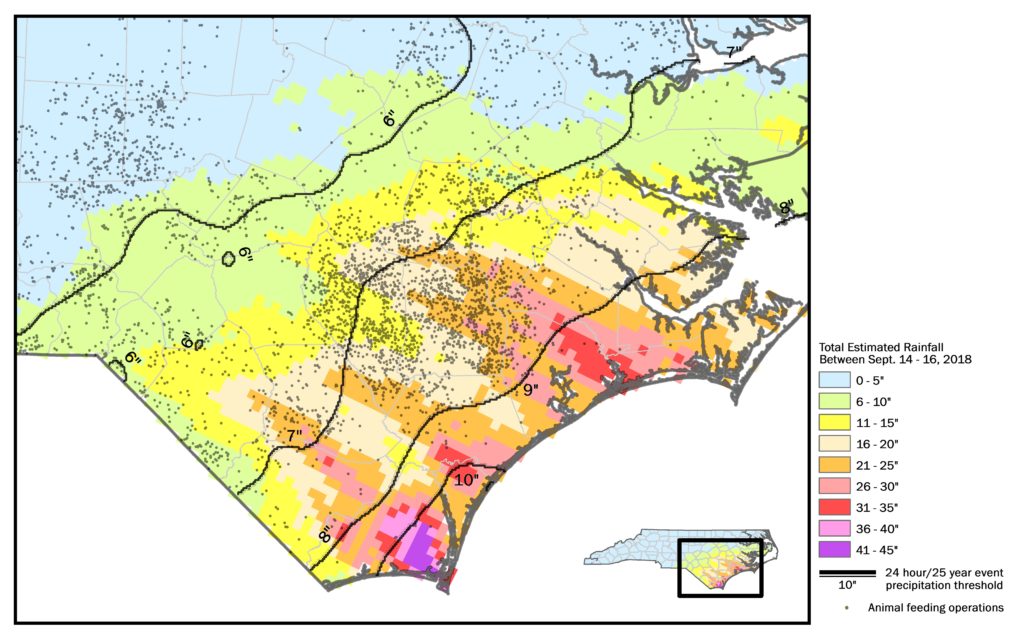
Source: EWG, from National Weather Service data
“It’s just a matter of time until another massive rain event happens again in the floodplain,” said Soren Rundquist, Director of Spatial Analysis at EWG. “How many scenes of swamped animal barns and breached manure pits do state leaders and the factory farm industry need to see before they realize producing and storing billions of pounds of animal waste in flood-prone areas was and is a bad decision?”
“Waste mismanagement at industrial animal agriculture operations threatens public health and environmental quality under sunny skies,” said Will Hendrick, staff attorney and manager of the Pure Farms, Pure Waters campaign at Waterkeeper Alliance. “That threat is disproportionately borne by communities of color or low wealth and it is exacerbated, given the concentration of production in the coastal plain, by increasingly frequent and severe storms like Hurricanes Matthew and Florence.”
EWG and Waterkeeper Alliance will continue our analysis of Hurricane Florence’s impact on CAFOs in North Carolina’s coastal plain.